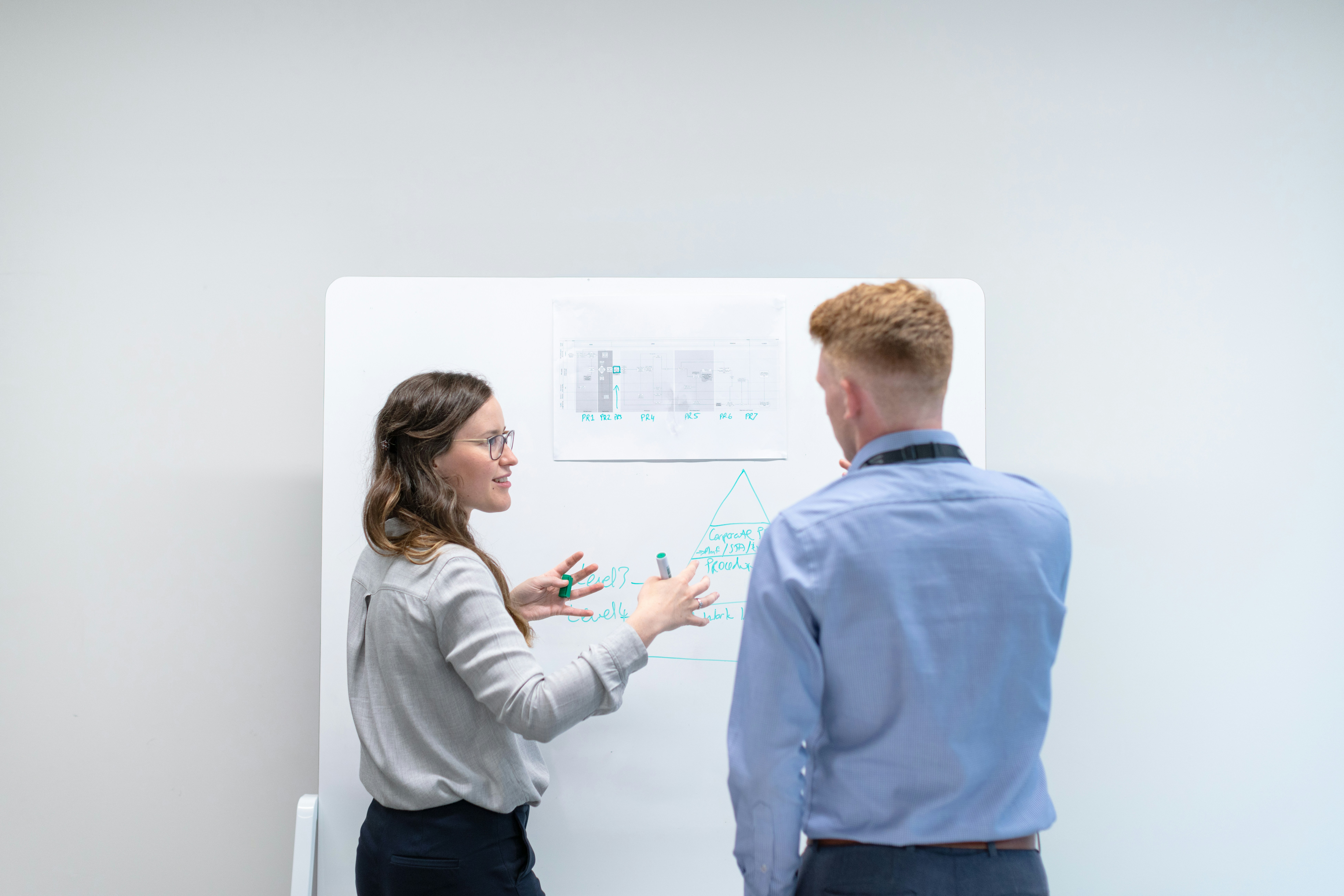
The study, coauthored by Jonathan Levav of Stanford Graduate School of Business and Melanie Brucks of Columbia Business School, finds that in-person teams generated more ideas than remote teams working on the same problem.
In a laboratory experiment conducted at Stanford, half the teams worked together in person and half online. The in-person teams generated 15% to 20% more ideas than their virtual counterparts. In a separate experiment involving almost 1,500 engineers at a multinational corporation, in-person teams came up with more ideas, and those ideas received higher ratings for originality.
The researchers say they’ve identified a reason online meetings generated fewer good ideas: When people focus on the narrow field of vision of a screen, their thinking becomes narrower as well. “If your visual field is narrow, then your cognition is likely to be as well,” Levav says. “For creative idea generation, narrowed focus is a problem.”
In contrast, people who meet in person get creative stimulation by visually wandering around the space they’re in, which makes them more likely to cognitively wander as well. “In a video interaction, you need to fix your gaze at the screen because otherwise you’re projecting to your partner that you’re looking at something else and distracted,” Levav says. But that distraction is actually useful when it comes to sparking ideas. “If you think about disruptive ideas, they come from putting together broad concepts that are seemingly unrelated.”
Levav, a professor of marketing who has studied how environmental cues affect people’s choices, cautions that these findings don’t mean that virtual meetings have no value. His study also found that teams meeting online did as well and possibly better than in-person teams when it came to selecting the best ideas.
The real lesson, Levav says, is that the costs and benefits of working remotely are more nuanced and less understood than most people realize.
“The shift to working more from home is here,” he says. “But the pandemic happened without giving us a chance to think about how to do remote working right. If we’re going to maintain this transition, we need to be deliberate about how we manage the process. That’s going to be the managerial challenge of the next several years.”
Interestingly, Levav and Brucks found that virtual meetings didn’t seem to hinder how well the participants got along. Using semantic analysis of how participants spoke to each other, they found that the virtual and in-person teams showed the same amount of mutual trust and social connection.
As remote work remains a fixture of many people’s lives, Levav says it would be worth exploring how virtual meetings work in other contexts, such as job interviews and larger group collaborations. But for now, he says, “We don’t yet know enough to make strident judgments about the superiority of working remotely versus in person. What our research shows is that there’s subtlety.” In other words, it’s too soon to zoom to conclusions.